Amazon FBA vs. FBM: A Strategic Analysis for Your Business Model
If you sell on Amazon, you’ll choose between Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM). With FBA, Amazon stores your inventory, picks, packs, ships, and handles returns-for a fee. With FBM, you manage storage, shipping, and customer service yourself.
Both models work-just in different situations. Your decision should reflect your product type, margins, order volume, and operational capacity. Many sellers even run a hybrid strategy: FBA for fast-moving, standard-size products that benefit from Prime, and FBM for bulky, niche, or slower-moving items where you want more control and lower carrying costs.
In this guide, we’ll break down FBA vs. FBM-key differences, benefits, trade-offs, and ideal use cases-so you can choose the most profitable, scalable fulfillment approach for your Amazon business.
What is Amazon FBA?
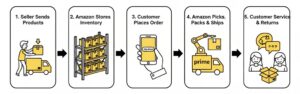
Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) is a service where sellers store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers, and Amazon handles the rest. When an order is placed, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the product directly to the customer. It also manages returns, refunds, and customer service, allowing sellers to focus on growing their business instead of handling logistics.
How Amazon FBA Works
Amazon handles storage, shipping and support-you focus on sales

Pros of Amazon FBA
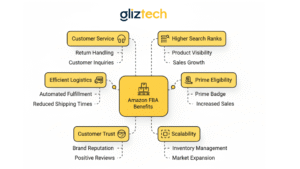
- Efficient Logistics
With Amazon FBA, sellers ship products to Amazon’s warehouses, and Amazon handles everything—storage, packing, shipping, and returns. This saves time, reduces workload, and ensures fast, reliable delivery that keeps customers happy. - Prime Eligibility
FBA products are eligible for Amazon Prime, giving customers access to fast and free shipping. Prime listings attract more buyers, boost visibility, and often lead to higher sales and conversion rates. - Customer Trust
Products labeled “Fulfilled by Amazon” instantly earn credibility. Shoppers trust Amazon’s reputation for speed and reliability, which increases purchase confidence and overall sales. - Scalability
FBA makes it easy to grow without worrying about space or staffing. Amazon’s massive fulfillment network can handle demand spikes smoothly, helping sellers expand efficiently. - Customer Service
Amazon’s 24/7 customer service team manages inquiries, returns, and refunds on behalf of sellers. This ensures professional support and a positive shopping experience while freeing sellers to focus on business growth. - Higher Search Rankings
Amazon’s algorithm favors FBA listings due to Prime shipping and strong customer satisfaction, giving FBA sellers better visibility and a higher chance to appear on the first search page. - Buy Box Advantage
FBA listings have a higher chance of winning the Buy Box—Amazon’s prime spot for purchases—because Amazon trusts its own fulfillment system. Winning the Buy Box can dramatically increase traffic and sales.
Cons of Amazon FBA
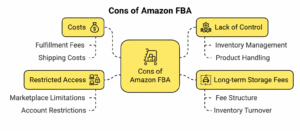
- High Fees
While FBA simplifies fulfillment, it comes at a cost. Sellers must pay storage and fulfillment fees, which can reduce profit margins—especially for low-priced or slow-selling products. Extra charges for labeling, inventory removal, or returns can also add up quickly. - Limited Control
With FBA, Amazon handles inventory, packaging, and shipping—meaning sellers have little influence over how their products are packed or presented. This can be a drawback for brands that value custom packaging or want to maintain a more personal touch. - Long-Term Storage Charges
Products sitting too long in Amazon’s warehouses incur additional long-term storage fees. These can eat into profits, particularly for seasonal or slow-moving inventory. Sellers must monitor stock levels and sell items before these charges apply. - Program Restrictions
Amazon’s FBA program has strict rules and eligibility requirements. Certain product categories need approval, and all items must meet Amazon’s detailed prep and labeling standards. Failing to comply can delay listings or lead to inventory being rejected.
Financial Implications of Amazon FBA
While Amazon FBA offers convenience and scalability, it comes with several costs that sellers must factor in. Beyond standard referral and selling plan fees, FBA sellers pay storage fees for keeping inventory in Amazon’s fulfillment centers and fulfillment fees for every order shipped. If products remain unsold for too long, long-term storage fees also apply, which can quickly cut into profits.
To stay profitable, sellers should closely monitor inventory turnover, avoid overstocking, and regularly analyze how FBA fees impact overall margins.
What is Amazon FBM?
Amazon FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant) means the seller is fully responsible for the fulfillment process – from storing inventory to packing and shipping orders directly to customers. Unlike FBA, where Amazon manages logistics and customer service, FBM sellers handle everything themselves.
To succeed with FBM, sellers must maintain organized inventory, use quality packaging, and ensure timely delivery that meets Amazon’s performance standards. They also manage returns, refunds, and customer communication, giving them full control over their operations and customer experience.
How Amazon FBM Works
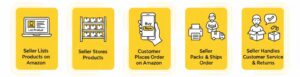
Pros of Amazon FBM
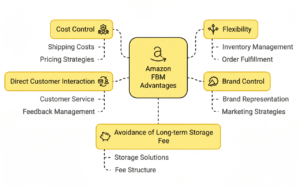
- Cost Control
FBM gives sellers more control over expenses since they handle storage, packing, and shipping themselves. By avoiding FBA fulfillment fees, sellers can reduce costs—especially beneficial for low-margin or custom products. - Flexibility
With FBM, sellers can choose how and where to store inventory, which shipping carriers to use, and how to manage customer service. This flexibility makes it easier to adapt to seasonal demand, product type, or changing market conditions. - Brand Control
FBM allows sellers to maintain full control over packaging and presentation. Custom boxes, inserts, or personal notes help strengthen brand identity and create a more memorable customer experience. - Direct Customer Interaction
Since sellers handle fulfillment and service directly, they can communicate with customers, resolve issues faster, and build stronger relationships through personalized attention and better responsiveness. - No Long-Term Storage Fees
Unlike FBA, FBM sellers don’t pay Amazon’s long-term storage charges. They can manage inventory at their own pace, store products cost-effectively, and avoid penalties for slow-moving or seasonal items.
Cons of Amazon FBM
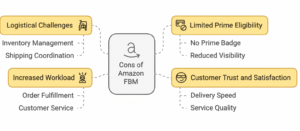
- Logistical Challenges
FBM sellers handle every step of fulfillment—storage, packing, and shipping. Without a strong logistics setup, this can become time-consuming and error-prone, especially during high order volumes. Inefficient inventory management or shipping delays can hurt performance metrics and customer satisfaction. - Limited Prime Eligibility
FBM listings typically don’t qualify for Amazon Prime, meaning they miss out on the visibility and conversion boost Prime products enjoy. Since many customers filter by “Prime,” this can reduce sales potential and competitiveness unless the seller qualifies for Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP). - Lower Customer Trust
Buyers often trust Amazon-fulfilled orders more than merchant-fulfilled ones. Slower delivery, inconsistent packaging, or less responsive customer service can lead to negative feedback, making it harder for FBM sellers to maintain strong ratings and repeat customers. - Higher Workload
FBM demands hands-on management—tracking inventory, packaging orders, handling returns, and responding to buyer messages. For small teams or solo sellers, this workload can quickly become overwhelming without automation or reliable third-party logistics support. - Seasonal Pressure
FBM sellers face challenges during peak seasons, when order volumes surge. Limited staffing or warehouse capacity can lead to delays and customer dissatisfaction. In slower months, managing unused inventory and storage space can also increase costs.
Financial Considerations for Amazon FBM
Running your business through FBM means taking full responsibility for fulfillment expenses. While you save on Amazon’s storage and fulfillment fees, several other costs come into play:
- Packaging Costs: Boxes, labels, tape, and protective materials add up, especially with high order volumes.
- Shipping and Delivery: You’ll cover carrier fees, delivery charges, and potential surcharges for expedited or international shipping.
- Returns Management: Handling product returns, restocking, and refunds requires time, labor, and sometimes additional shipping costs.
- Customer Service Tools: To maintain response speed and quality, you may need automation software or support systems for managing customer inquiries.
- Other Logistics Expenses: Gas, transport, and warehouse operations can increase overhead, particularly if you self-manage inventory and deliveries.
Proper budgeting and cost tracking are crucial for FBM sellers to ensure profitability while maintaining a smooth customer experience.
Choosing Between FBA and FBM: Which is Right for You?
The ideal fulfillment model depends on your product type, sales volume, and how much control you want over operations. Here’s a simple breakdown to help you decide:
FBA is best for you if:
- You sell in high volume: Amazon’s network handles large order loads efficiently.
- You prefer a hands-off approach: FBA manages storage, packaging, shipping, and customer service.
- You’re a new seller: No need to build a logistics system—Amazon takes care of it.
- You lack warehouse space: Store your inventory in Amazon’s fulfillment centers.
- You sell standard-sized products: FBA is more cost-effective for smaller, fast-moving items.
- You’re fine with the fees: You value convenience and scalability over direct cost control.
FBM is better suited if:
- You sell slow-moving items: Avoid costly long-term FBA storage fees.
- You have logistics experience: You already manage inventory, shipping, and returns efficiently.
- You work with shipping partners: You can negotiate lower rates or use your own delivery network.
- You have your own storage: Utilize existing warehouse space to save on Amazon’s storage fees.
- You sell bulky or unique products: FBM offers flexibility for oversized or specialized inventory.
- You focus on profit margins: Keeping control over fulfillment costs can increase profitability.
In short:
- FBA(Fulfillment by Amazon) = convenience, Prime eligibility, and scalability.
- FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant)= control, flexibility, and potentially higher margins.
Many successful sellers use a hybrid approach-FBA for fast movers and FBM for large or niche products-to balance cost and performance.
Conclusion
Choosing between Amazon FBA and FBM depends on your business goals, product type, and operational capacity. FBA is perfect for sellers who want convenience, faster delivery, and access to Amazon Prime customers, even if it means paying higher fees. On the other hand, FBM suits sellers who prefer full control, lower costs, and flexibility in how they manage orders and customer service.
For many sellers, the most effective strategy is a hybrid approach—using FBA for fast-moving, standard items and FBM for oversized or slower-selling products. Ultimately, the best choice is the one that maximizes your profit while aligning with your business model and long-term growth strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What’s the main difference between FBA and FBM?
FBA means Amazon handles storage, shipping, and customer service for a fee, while FBM means you manage everything yourself. - Which is more profitable — FBA or FBM?
It depends on your product type and sales volume. FBA can boost sales with Prime access, while FBM helps cut costs if you manage logistics efficiently. - Can I use both FBA and FBM at the same time?
Yes. Many sellers use a hybrid approach — FBA for fast-moving products and FBM for bulky or slow-selling items. - Do FBM sellers get the Prime badge?
Not by default. Only sellers who qualify for Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) can display the Prime badge while fulfilling orders themselves. - Is FBA better for beginners?
Yes. FBA is ideal for new sellers who want a simple, hands-off way to manage fulfillment and focus on growing their business.

